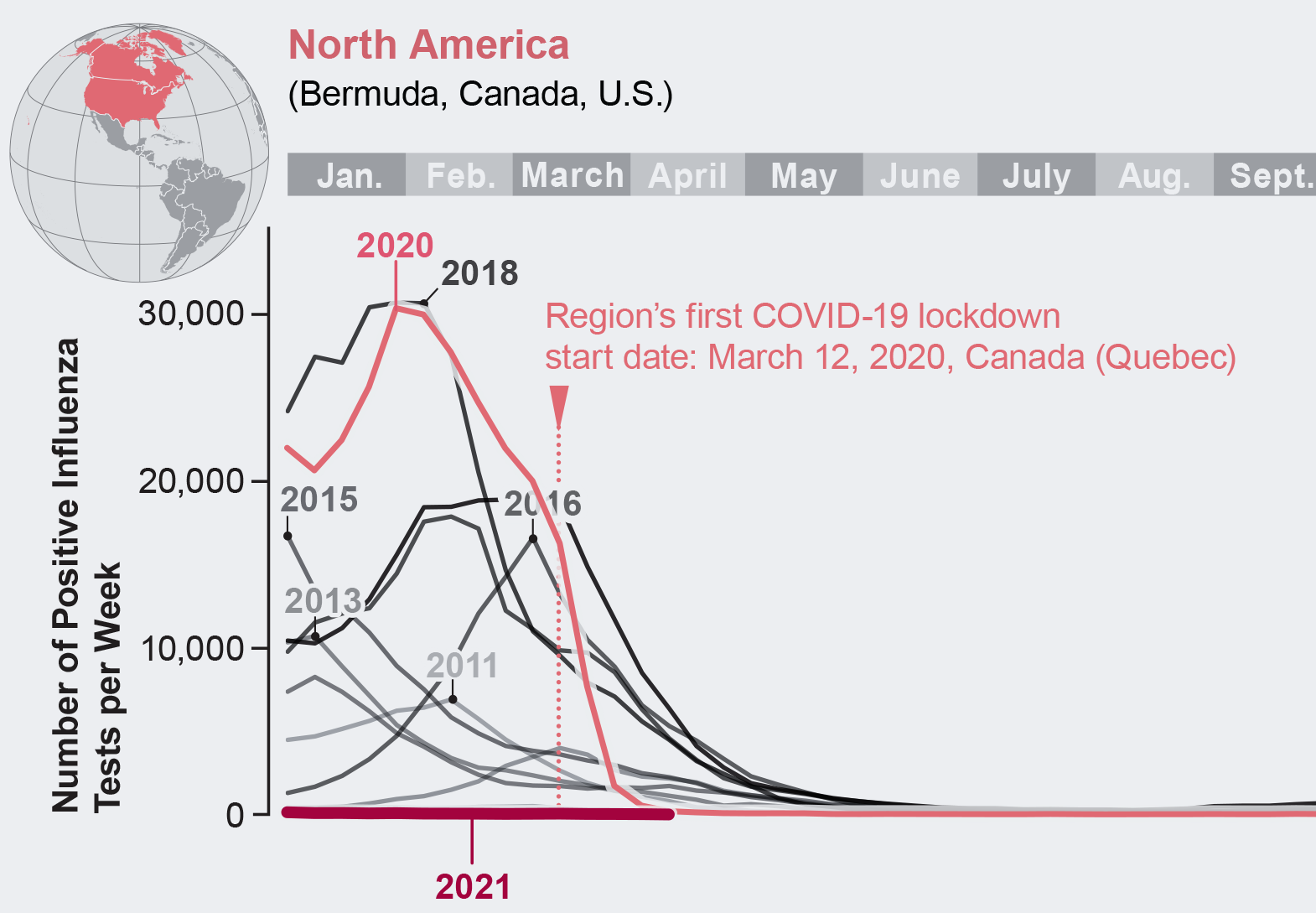
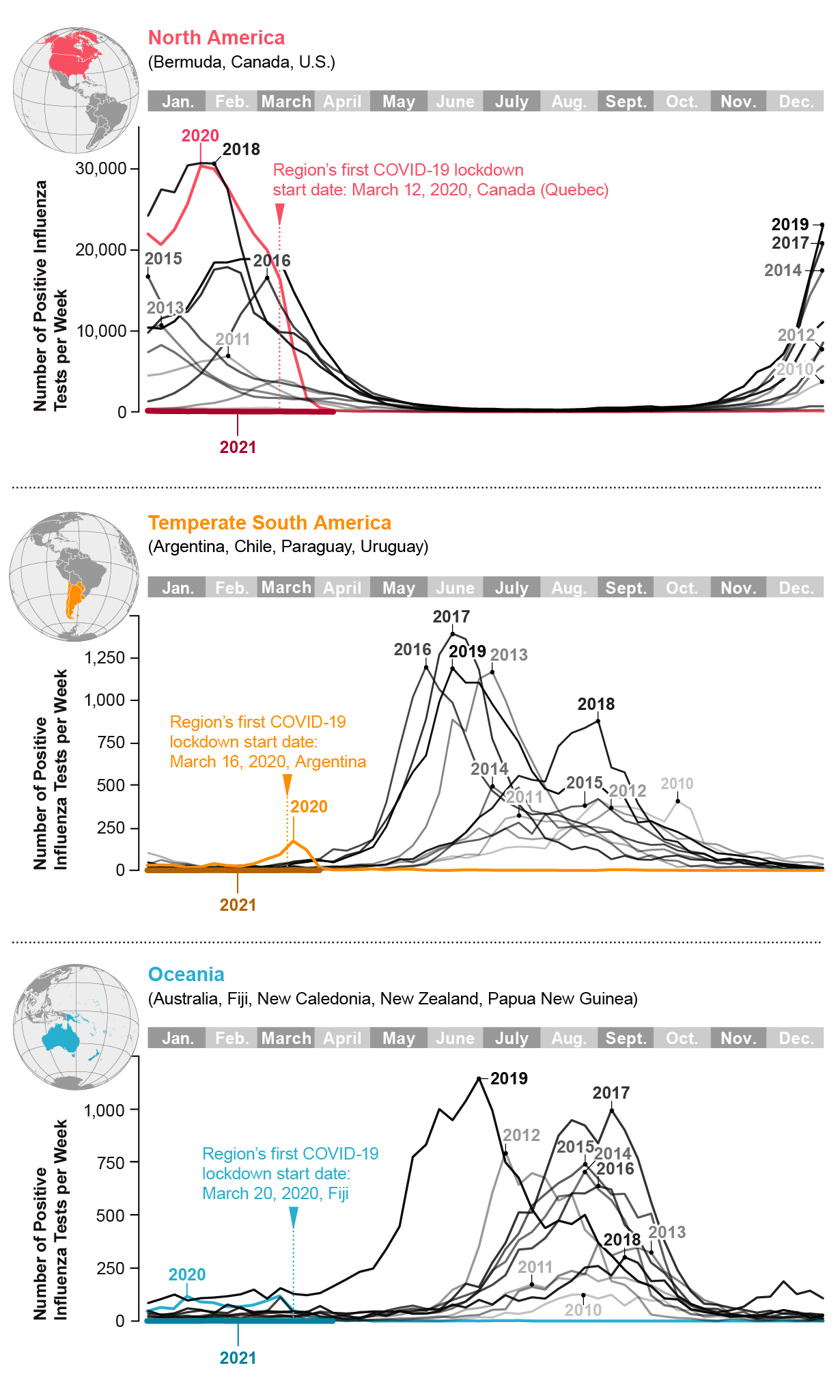
Because each year’s flu vaccine is based on strains that have been circulating during the past year, it is unclear how next year’s vaccine will fare, should the typical patterns of the disease return. The WHO made its flu strain recommendations for vaccines in late February as usual, but they were based on far fewer cases than in a common year. At the same time, with fewer virus particles circulating in the world, there is less chance of an upcoming mutation, so it is possible the 2021–2022 vaccine will prove extra effective.
Public health experts are grateful for the reprieve. Some are also worried about a lost immune response, however. If influenza subsides for several years, today’s toddlers could miss a chance to have an early-age response imprinted on their immune system. That could be good or bad, depending on what strains circulate during the rest of their life. For now, future flu transmission remains a roll of the dice.
Influenza Cases Worldwide, by Region
The World Health Organization tracks influenza transmission in 18 zones. Three of those regions appear here. Only people who get tested for influenzalike illnesses—typically about 5 percent of individuals who fall ill—are tallied.


No comments:
Post a Comment